Body-Focused Repetitive Behaviors (BFRBs) is an umbrella term for a chronic behavior that causes a person to consistently cause physical damage to oneself through a compulsive act in order to relieve anxiety. BFRBs are pathological grooming behaviors that are thought to be driven by similar impulsive urges, linking them together but manifesting differently in the following ways:
Skin-Related BFRBs
Dermatillomania/ Excoriation Disorder:
Excoriation disorder is a mental health condition that manifests through the compulsive urge to pick at one’s own skin.

Dermatodaxia:
Those with dermatodaxia compulsively bite, gnaw, or chew skin on their body.
Previous terms used to describe hand-biting is dermatophagia– or skin eating- and wolf-biter syndrome, both which are stigmatizing to individuals with this condition.
Scab eating disorder:
This disorder coincides with other skin-related BFRBs, often taking place last in completing the compulsion. Critically categorized as auto-cannibalism along with nail and hair-eating, scab eating disorder can be mistaken for an eating disorder.
Rhinotillexomania:
While most common in children, rhinotillexomania (compulsive nose-picking) affects many adults on a universal scale.
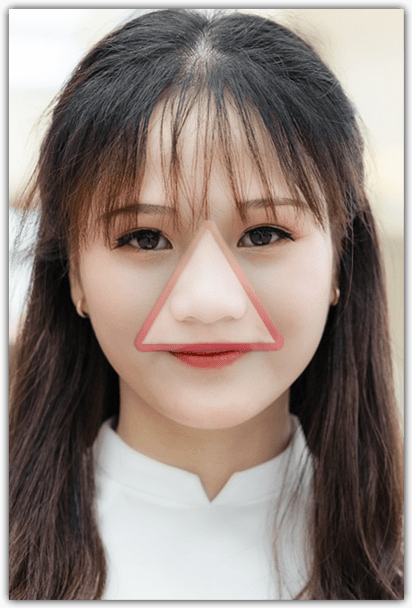
Most people who pick their nose habitually do not have a BFRB; however, it becomes problematic when a sufferer continually causes damage to his/ her nose and is unable to stop the compulsive behavior, much like dermatillomania, and both are treated in the same manner. Those with rhinotillexomania are at a greater risk of serious infections because of the danger triangle, which consists of sharing the same blood flow from the bridge of the nose to each corner of the mouth making it easier for infections to travel to the brain.
Oral BFRBs
Morsicatio buccarum:
Derived from the Latin words, morusus meaning “bite” and bucca meaning “cheek”, this condition involves repetitive biting of the cheek. A dental examination can rule out structural issues with the jaw as a root cause of the BFRB. Acrylic prosthesis can serve as barriers from biting surfaces of the teeth while protecting the cheek, tongue, and labial mucosa.

Morsicatio labiorum:
This condition is characterized by a person biting, chewing, or sucking their inner lip.
When teeth scrape up against the inside of the cheek, cells create a protective coating called keratin. In serious cases, these calloused areas may need to be surgically treated by your dentist or oral surgeon. Laser treatments are one of the newer procedures that cauterizes the keratinized tissue off, leaving a smooth surface.
Morsicatio linguarum:
Chronic tongue biting is a behavior often seen by dentists. Over an extended period of time, this condition can lead to difficulty in chewing and speech. As the skin thickens and enlarges, the individual may find it increasingly difficult to masticate or open their mouth wide. Tissue damage may vary from minor to extensive abrasions, ulcers, and hyperkeratosis.
Nail Biting and Picking
Onychophagia:
One of the most common BFRBs, onychophagia is the medical term for compulsive nail-biting.
This disorder is the most socially acceptable and often considered a “habit”. Complications may occur when nails are bitten down to the cuticle, causing debilitating pain and potential for infection.
Onychotillomania:
Coined by Polish dermatologist Jan Alkiewicz, onychotillomania is the compulsive need to pick at or tear off one’s nails.
Hair-Related BFRBs
Trichotillomania:
Trichotillomania causes one to pull out hairs from their scalp, eyebrows, eyelashes, or facial hair.
While these areas are commonly pulled from, trichotillomania expands to the compulsive pulling of any bodily hair.
Trichophagia:
Those with trichophagia may eat the hair off of brushes (their own or others) or chew their hair and ingest it. It often coincides with trichotillomania after a pull as part of a ritual in order to achieve relief from anxiety. This disorder may lead to serious complications from hairs accumulating in the stomach (trichozeboars), resulting in surgical removal.
Trichotemnomania:

This behavior is the conscious act of compulsively shaving or cutting one’s own hair.
A sufferer can be drawn to these behaviors as stress relievers because it can signify a form of cleansing or need for perfection.
Other
Mucus-Fishing Syndrome:
The chronic urge to pull strands of mucus strands from the eyelids, which may lead to eye irritation or infection.
Mental Health & Social Impact
People with body-focused repetitive behaviors (BFRBs) are likely to experience shame and embarrassment because of these disorders, even caused by mental health professionals.
Engaging in BFRBs can be time consuming; trying to hide its aftermath often increases a person’s anxiety, triggering more urges, and feeding into a vicious cycle.
The social impact of BFRBs can be devastating. Having a BFRB can be isolating because of a lack of understanding, compassion, education, or acceptance of these conditions. Dealing with the unintended consequences of a BFRB can be distressing enough to negatively affect a person’s mental health and cause them to withdraw from daily activities.
With at least 5% of the population living with a BFRB, gaining access to a specialized treatment provider is difficult in many parts of the world. The TLC Foundation for BFRBs’ database includes professionals who have completed the Clinical Training in CBT-Based Treatment for Body-Focused Repetitive Behaviors course through the TLC’s Professional Training Institute, some who offer services via webcam.
